Sunday, February 1, 2015
DC Circuits: Calculating Voltage Drops and Total Current Problem #1
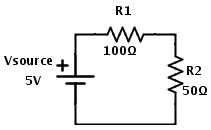
Two resistors in series, 100 Ohms and 50 Ohms in values, are connected in series to a 5 Volts source. What is the voltage drop across each of the resistor? What is the total current I?Firstly, we need to draw the circuit to better understand it.
Solution:
I = \frac{V}{R}
Calculate the total resistance. Learn how to calculate total resistance here.
R_T = R_1+R_2
R_T = 100\Omega+50\Omega
R_T = 150\Omega
Solving for the total current,
I_T = \frac{V}{R}
I_T = \frac{5V}{150\Omega}
I_T = 0.033333333333 Amperes = 33.333333333333x10^{-3} Amps
I_T = 33.33 mA
Solving for voltage drops across the resistors,
V_{R1} = (I_T)(R_1)
V_{R1} = (33.33 mA)(100\Omega)
V_{R1} = 3.33V
V_{R2} = (I_T)(R_1)
V_{R2} = (33.33 mA)(50\Omega)
V_{R2} = 1.67V
We use the same current value in solving both voltage drops because elements connected in series have equal currents flowing through them. The sum of all the voltage drops is equal to the voltage source.
V_{source} = 3.33V+1.67V
V_{source} = 5V
If you have questions about this example, place a comment below.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments
(
Atom
)
No comments :
Post a Comment